Prompt Engineering for BIM Development
Master the art of communicating with Cursor AI to accelerate your Building Information Modeling workflows.
Understanding Cursor's AI Capabilities
Cursor integrates multiple AI models to assist with code generation, completion, and problem-solving. Based on the official Cursor documentation, Cursor can:
- Generate code from natural language descriptions
- Complete code with context-aware suggestions
- Debug issues by understanding your codebase
- Explain code and provide documentation
- Refactor code for better performance and readability
DCMvn Cursor Pro Subscription
At DCMvn, we have a Cursor Pro subscription with the following features:
- 500 premium requests per month shared across the team
- Multiple AI model access with different cost structures
- Enhanced performance for complex BIM development tasks
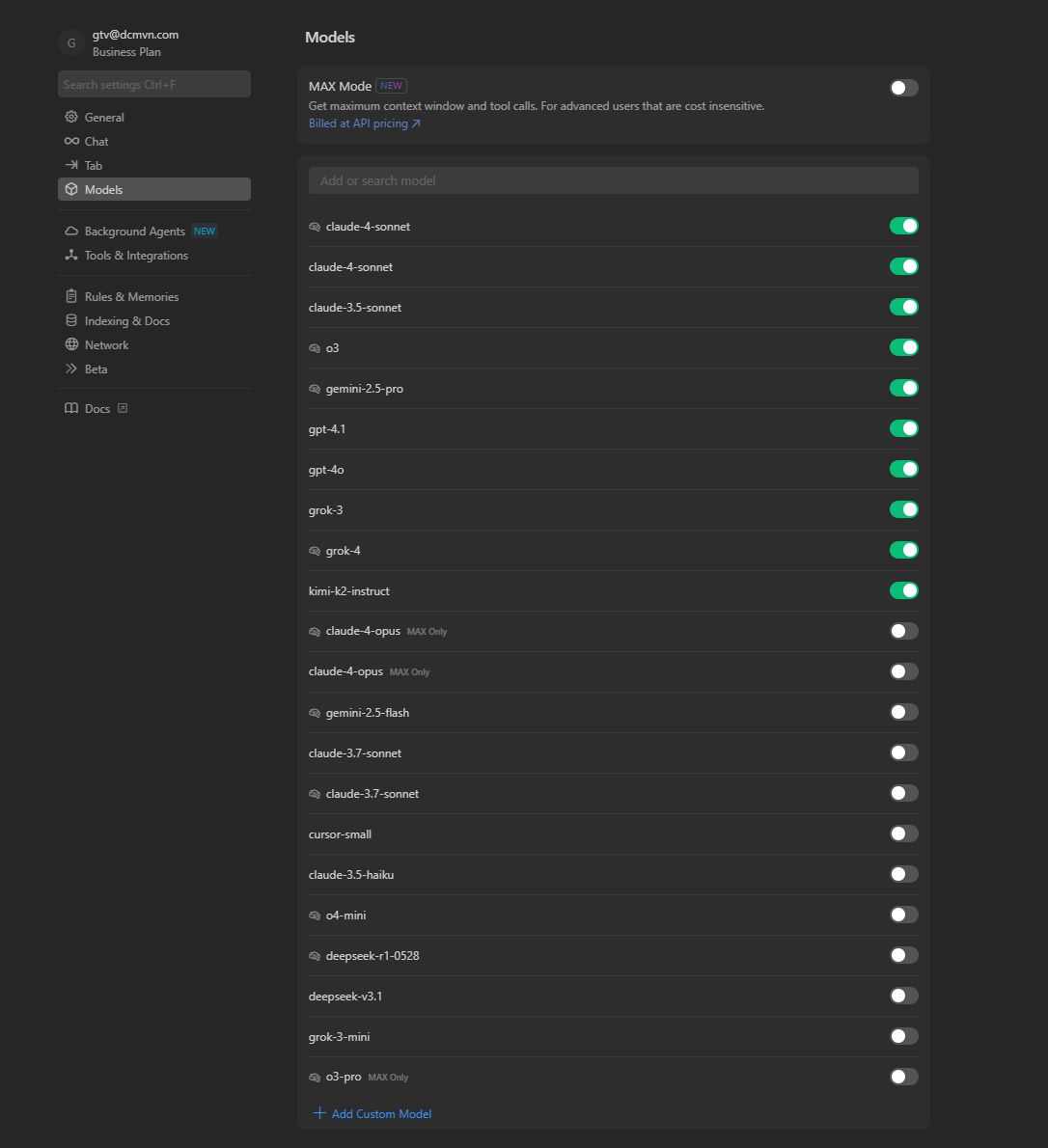
Available AI models in Cursor Pro showing different capabilities and request costs
Model Selection and Request Costs
Different AI models have varying request costs that impact your monthly allocation:
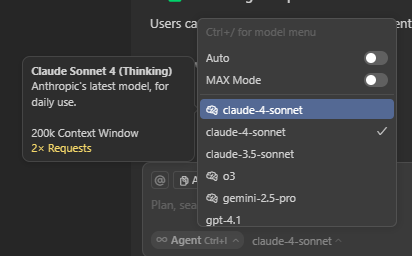
Model selection interface showing cost implications for different AI models
Current Model Pricing (Subject to Change):
- Claude Sonnet 4: 1 premium requests per query (excellent for both daily use and complex BIM logic)
- Claude Sonnet 4 Thinking: 2 premium requests per query (best for architectural understanding)
- Claude Opus 4: Max Mode (high cost) for complex advanced & detailed architecture prompt
- Other Models: 1 premium request per query (standard pricing)
- Max Mode: High premium request cost - use sparingly for complex multi-file operations
With 500 premium requests per month, plan your AI usage strategically:
- Use Claude Sonnet 4 Thinking for complex Revit API problems (2 requests each)
- Reserve Max Mode for critical architectural refactoring (high cost)
- Consider model capabilities vs. cost for routine tasks
- Monitor your request usage throughout the month
Usage Dashboard
Monitor your AI model usage through the Cursor Dashboard.
📊 Dashboard Guide: Learn about usage monitoring and model selection in LLMs for Coding Agents
Indexing and Documentation Integration
Cursor's indexing system provides crucial context for AI assistance.
🔍 Indexing Setup: Configure codebase indexing for optimal performance in Project Setup
Strategic Prompt Planning for Limited Requests
Given DCMvn's 500 premium requests per month, effective prompt engineering becomes crucial for maximizing value:
Request Budgeting Strategy
High-Value Scenarios (Use Premium Models):
- Complex Revit API architecture - Use Claude Sonnet 4 Thinking (2 requests)
- Multi-file refactoring - Use Claude Sonnet 4 (1 request)
- Advanced MVVM patterns - Use Claude Sonnet 4 (1 request)
- Critical debugging - Use appropriate model based on complexity
- Use Max Mode (high cost, but comprehensive) when you have a complete blueprint (the most detail instruction as much as possible)
Medium-Value Scenarios (Standard Models):
- Parameter extraction logic - Use standard models (1 request)
- Simple pyRevit tools - Use standard models (1 request)
- Documentation generation - Use standard models (1 request)
Low-Value Scenarios (Avoid Premium):
- Basic syntax questions - Use ChatGPT (free)
- Simple code completion - Use Tab completion (free)
- Quick clarifications - Use ChatGPT (free)
Monthly Planning Tips
- Plan complex tasks early in the month when requests are available
- Batch similar queries to maximize context efficiency
- Use incremental development to refine prompts before premium submission
- Reserve Max Mode for end-of-sprint architectural work
- Monitor usage through Cursor's request counter
Cursor Context Reference
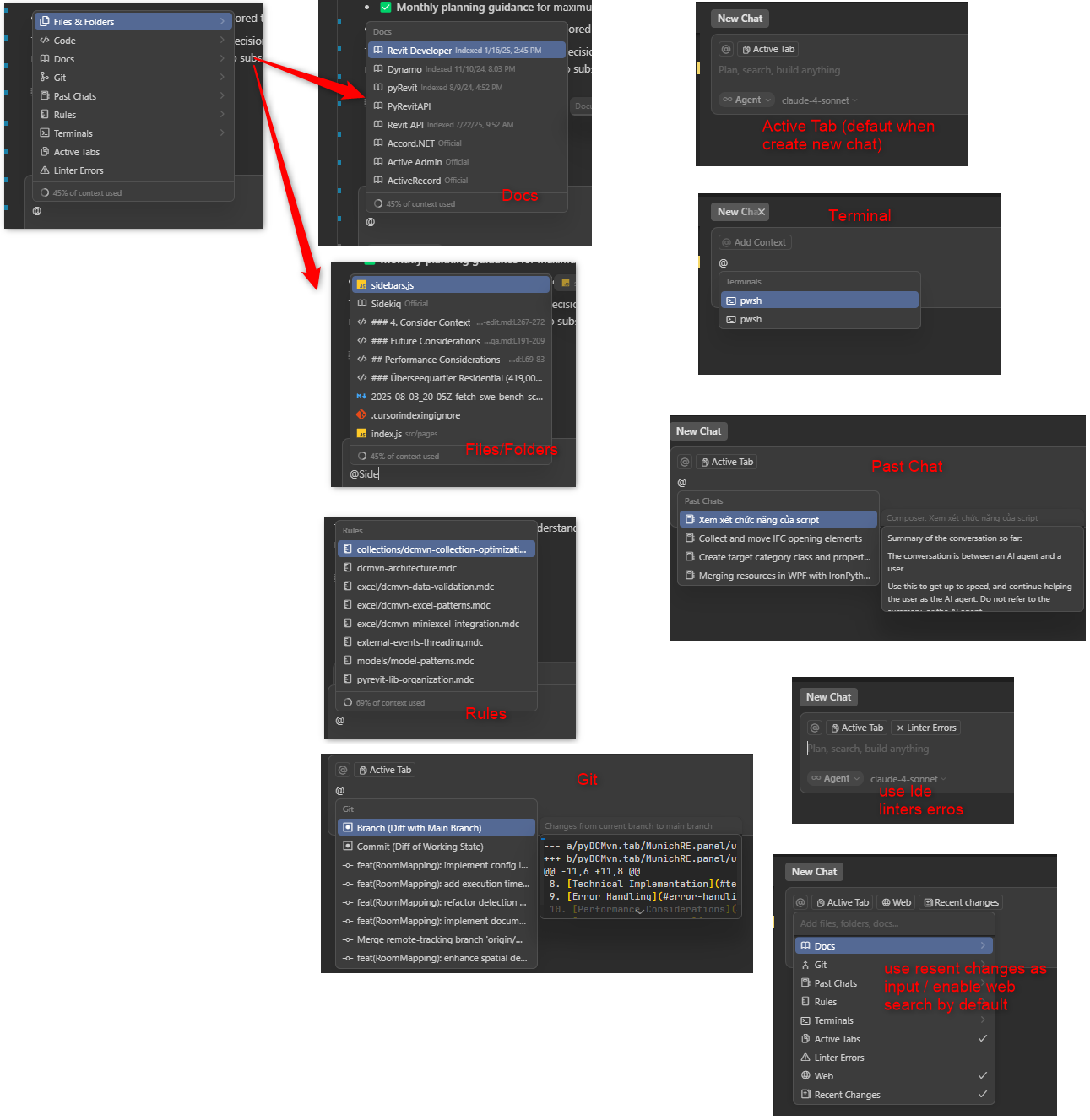
Cursor Context Reference showing the different context features available
Rules and Memories
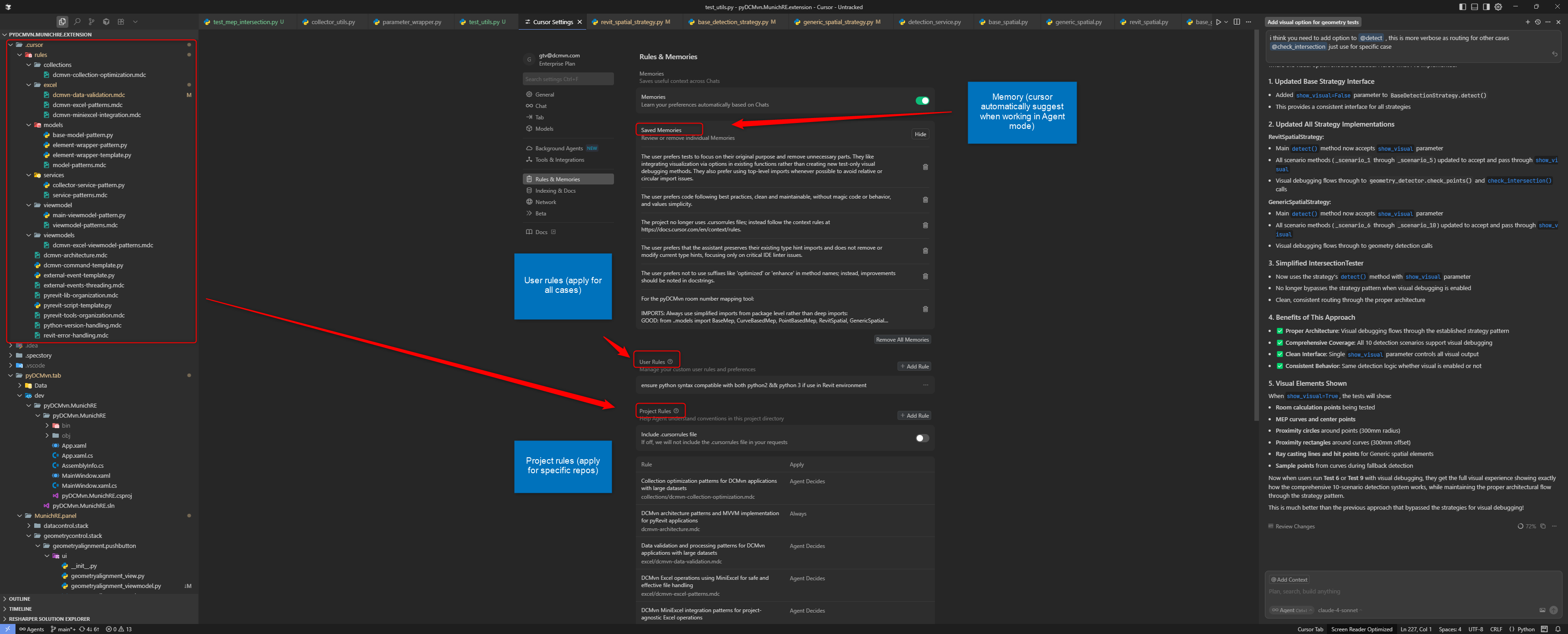
Cursor's Rules and Memories interface for configuring AI behavior and maintaining context across sessions
Core Prompt Engineering Principles
1. Be Specific and Contextual
❌ Vague Prompt
"Create a wall function"
✅ Specific BIM Prompt
"Create a C# Revit API external command that collects all interior walls
on Level 1, extracts their wall type, thickness, and fire rating parameters,
then exports the data to Excel with proper formatting and error handling."
2. Include Technical Context
❌ Generic Request
"Make a script to process building data"
✅ BIM-Specific Context
"Create a pyRevit script that processes IfcSpaceType to extract
space data including area, volume, and occupancy classification according
to buildingSMART standards, then generates a compliance report for
accessibility requirements."
3. Specify Error Handling and Edge Cases
❌ Basic Request
"Get room areas from Revit"
✅ Robust Request
"Create a Revit API function that safely extracts room areas, handling
unplaced rooms, rooms with zero area, linked files, and design options.
Include try-catch blocks for transaction errors and parameter access failures."
BIM-Specific Prompt Patterns
Revit API Development Prompts
Plugin Architecture
"Generate a complete Revit external command structure with:
- Proper attribute decorations for manual transactions
- Error handling with user-friendly messages
- Progress reporting for long operations
- Undo functionality
- Resource cleanup and disposal patterns"
MEP Element Collection and Filtering
"Create a filtered element collector that finds all duct fittings
where the system type is 'Supply Air' and the fitting size is greater
than 12 inches diameter, with error handling for missing parameters."
Parameter Management
"Build a parameter utility class that safely reads and writes Revit
parameters with type checking, handles shared vs instance parameters,
and includes methods for parameter creation and validation."
IFC Processing Prompts (Standalone Python Scripts)
Schema Navigation (External Script)
"Create a standalone Python script using ifcopenshell that traverses the spatial
hierarchy from IfcProject > IfcSite > IfcBuilding > IfcBuildingStorey >
IfcSpace and extracts MEP system data according to IFC4x3 schema.
The script should run independently without Revit."
MEP System Extraction (External Script)
"Develop a standalone Python function using ifcopenshell that extracts all
HVAC system information from IFC files, including duct networks, equipment,
and flow rates. Handle missing properties gracefully and export to Excel."
BCF Issue Processing (External Script)
"Build a standalone Python tool using ifcopenshell and BCF libraries that:
- Reads BCF files and extracts issue locations
- Correlates issues with IFC element GUIDs
- Generates HTML reports with issue summaries
- Runs without any CAD software dependencies"
MEP Data Analysis Prompts
Duct Sizing Analysis
"Create a pyRevit script that analyzes duct sizing in the current model:
- Collects all ductwork and their flow parameters
- Identifies oversized or undersized ducts based on velocity
- Generates a simple HTML report with findings
- Exports results to Excel with color-coded recommendations"
Equipment Inventory
"Develop a MEP equipment inventory tool that:
- Collects all mechanical equipment in the model
- Extracts manufacturer, model, and capacity information
- Creates equipment schedules with proper formatting
- Exports to Excel with equipment photos if available"
Cost-Effective Prompt Strategies
Maximizing Value per Request
Since each premium request counts, structure your prompts to get maximum value:
✅ Comprehensive Single Request
"Create a complete pyRevit tool for MEP duct analysis that:
1. Collects all ductwork with flow parameters
2. Calculates velocity and pressure drop
3. Identifies sizing issues with recommendations
4. Exports results to Excel with formatting
5. Includes error handling and progress reporting
6. Follows DCMvn coding standards and MVVM patterns"
❌ Multiple Separate Requests
Request 1: "How do I collect duct elements?"
Request 2: "How do I get flow parameters?"
Request 3: "How do I calculate velocity?"
Request 4: "How do I export to Excel?"
Request 5: "How do I add error handling?"
Batch Processing Prompts
When using premium models, combine multiple related tasks:
"For the MEP coordination project, provide:
1. Revit API code for clash detection between ducts and beams
2. Parameter extraction for conflict resolution
3. Report generation with clash locations and recommendations
4. Integration patterns with our existing MVVM framework
Include complete error handling and follow our project structure."
Advanced Prompt Engineering Techniques
1. Incremental Development
Start with a basic structure and refine:
Step 1: "Create a basic pyRevit script that displays duct count"
Step 2: "Enhance the script to collect all ducts and their flow rates"
Step 3: "Add parameter extraction for duct system type and size"
Step 4: "Include Excel export functionality with flow analysis"
Step 5: "Add error handling and progress reporting for large systems"
2. Template-Based Prompts
Use established patterns:
"Using the standard Revit API transaction pattern, create a [FUNCTION]
that [ACTION] for [ELEMENT TYPE] elements, handling [ERROR CONDITIONS]
and providing [USER FEEDBACK]."
Example:
"Using the standard Revit API transaction pattern, create a family loader
that batch loads structural steel families for beam elements, handling
missing files and name conflicts and providing progress feedback to users."
3. Multi-Model Prompts
For complex scenarios:
"Create a federated model analysis tool that:
1. Loads architectural, structural, and MEP Revit models
2. Aligns coordinate systems using shared coordinates
3. Detects model inconsistencies across disciplines
4. Generates an interdisciplinary coordination report
5. Exports issues to BIM 360 or ACC for resolution tracking"
4. Performance-Optimized Prompts
Request efficient solutions:
"Optimize this Revit element collection for large models (10,000+ elements):
- Use appropriate filters before ToElements()
- Implement batch processing for parameter access
- Include memory management for large datasets
- Add cancellation tokens for user interrupt
- Implement progress reporting every 100 elements"
Cursor-Specific Features for BIM
Tab Completion Optimization
// Start typing common BIM patterns and let Tab complete:
FilteredElementCollector collector = new // Tab suggests complete pattern
using (Transaction trans = new // Tab provides transaction boilerplate
if (element.get_Parameter( // Tab suggests common parameters
AI Chat Integration
Use the AI chat for complex questions:
"How do I handle circular references when traversing MEP system connections?"
"What's the most efficient way to update 1000+ family parameters in Revit?"
"Explain the difference between IfcSpace and IfcZone in IFC4 schema"
Codebase Understanding
Leverage Cursor's project awareness:
"Based on my existing ElementUtils class, create a similar utility for
handling MEP elements that follows the same patterns and error handling."
"Update all my Revit commands to use the new logging framework I've
implemented in the Logger.cs file."
Testing and Validation Prompts
Standalone Testing
"Create a standalone Python test script that validates MEP data processing logic:
- Use sample dictionaries to simulate duct data
- Test flow rate calculations without Revit dependencies
- Include edge cases like zero flow and missing parameters
- Generate test reports that can run on any Python environment"
Code Review
"Review this Revit API code for:
- Memory leaks and proper disposal patterns
- Thread safety issues
- Performance bottlenecks
- Compliance with Autodesk API best practices
- Error handling completeness"
Common Development Scenarios
Simple HTML Reports
"Create a pyRevit tool that generates simple HTML reports:
- Collects MEP equipment data from the model
- Creates formatted HTML tables with equipment information
- Includes basic styling with embedded CSS
- Show reports to user within Id linkify using pyRevit ouput window"
Excel Data Operations
"Build a pyRevit utility for Excel data operations:
- Read MEP equipment specifications from Excel files
- Update Revit element parameters based on Excel data
- Export duct analysis results to formatted Excel sheets
- Handle Excel file locking and error conditions gracefully"
SQLite Database Integration
"Design a simple database integration tool:
- Create SQLite database for storing MEP system data
- Insert duct and equipment information from Revit models
- Query database for reports and analysis
- Export query results to Excel or CSV formats"
🤖 AI Agent Guidelines
When to Use AI Agent
AI Agent is most effective for:
- Boilerplate code generation - Standard Revit API patterns, transaction templates
- Standard pattern implementation - MVVM structures, event handlers, common utilities
- Documentation writing - Code comments, API documentation, user guides
- Code review and optimization - Code analysis and improvement suggestions
- Refactoring existing code - Code cleanup, pattern modernization
- Data processing logic - Parameter extraction, filtering, calculations
- Simple HTML reports - Basic formatting and layout generation
- Excel operations - Data import/export, formatting utilities
Cursor settings showing how to maintain consistent behavior when working with AI Agent
When to Review Carefully
Always review AI-generated code carefully before accepting changes. AI can introduce subtle bugs, security vulnerabilities, or unintended modifications that may not be immediately apparent.
Requires Extra Scrutiny:
- Security-sensitive code - Authentication, data validation, file operations
- Performance-critical sections - Large dataset processing, memory management
- Complex business logic - Custom algorithms, calculation formulas
- Integration with external systems - APIs, databases, third-party services
- Error handling edge cases - Exception management, fail-safe mechanisms
- Revit API transactions - Model modifications, element creation/deletion
- Parameter manipulation - Shared parameters, family parameters
- Memory management - IDisposable objects, large collections
- Threading operations - Async/await patterns, background processing

Example of unnecessary changes that can occur - always review AI suggestions carefully to avoid unintended modifications
Things to Avoid - Critical Warning Signs
Never blindly accept AI-generated code that includes these patterns without thorough review:
🚨 High-Risk Code Patterns
Security Vulnerabilities:
# ❌ DANGER: Direct file path construction
file_path = user_input + ".txt"
# ❌ DANGER: SQL injection potential
query = "SELECT * FROM table WHERE id = " + str(user_id)
# ❌ DANGER: Unvalidated external input
os.system(user_provided_command)
Performance Issues:
# ❌ DANGER: Inefficient element collection
for elem in FilteredElementCollector(doc).ToElements(): # slow, loads all
process_element(elem)
# ❌ DANGER: Multiple transaction calls
for elem in elements:
with Transaction(doc, "Update") as t: # inefficient transaction usage
t.Start()
modify_element(elem)
t.Commit()
# ❌ DANGER: Large data processing without progress
all_walls = FilteredElementCollector(doc).OfClass(Wall).ToElements() # Memory intensive
Revit API Misuse:
# ❌ DANGER: Modifying model outside transaction
element.Name = "NewName" # Will fail - no transaction
# ❌ DANGER: Accessing parameters without null check
value = element.get_Parameter(param).AsString() # NullReference risk
# ❌ DANGER: Ignoring element state
if room.Area > 0: # Unplaced rooms have Area = 0, wrong logic
process_room(room)
🔍 What to Verify Before Accepting
Code Quality Checks:
- Error handling - Are try-catch blocks appropriate?
- Null checking - Are all object references validated?
- Resource disposal - Are IDisposable objects properly disposed?
- Transaction usage - Are model modifications wrapped correctly?
- Performance impact - Will this scale with large models?
- Input validation - Are user inputs properly validated?
- Memory management - Are large collections handled efficiently?
BIM-Specific Checks:
- Element existence - Are elements checked before processing?
- Parameter availability - Are parameters validated before access?
- Unit consistency - Are measurement units handled correctly?
- Coordinate systems - Are transformations applied correctly?
- Family context - Does code work in both project and family environments?
- Version compatibility - Will this work across Revit versions?
Quality Gates for AI-Generated Code
Mandatory Requirements:
- Performance benchmarks must be met for large model operations
- Security scans must pass for any external data handling
- Code must follow established patterns from project standards
- Manual code review by senior developer required
- Integration testing in realistic BIM environments
- Documentation must be complete and accurate
- Functional testing with representative Revit models
Acceptance Criteria:
✅ Code executes without errors in Revit environment
✅ No security vulnerabilities detected
✅ Performance meets project benchmarks
✅ Follows team coding standards
✅ Includes appropriate error handling
✅ Documentation is complete and clear
✅ Manual review completed and approved
✅ Tested with representative BIM models
Best Practices Summary
Technical Requirements
- Always specify the context (Revit API, IFC, MEP, etc.)
- Include error handling requirements in your prompts
- Request specific output formats (Excel, PDF, IFC, etc.)
- Mention performance considerations for large models
- Ask for documentation and comments in generated code
- Specify user experience requirements (progress bars, messages)
- Include compliance requirements (building codes, standards)
- Request validation scenarios for quality assurance
Cost Management (DCMvn Specific)
- Plan premium requests strategically - batch related queries
- Use comprehensive prompts - get maximum value per request
- Use Claude Sonnet 4 at daily use - use Claude Sonnet 4 for daily use, it's strong in both daily use and complex BIM logic (consider Gpt-4o for basic questions with more context window size)
- Consider Claude Sonnet 4 Thinking (2 requests) for complex BIM logic with advanced architecture
- Monitor monthly usage - track requests through Cursor interface
- Reserve Max Mode for critical architectural work only (high cost, you may loose all 500 premium requests with few questions)
- Use free features first - Tab completion, ChatGpt for prompt engineering suggestions
Resources
- Cursor Documentation - Official Cursor features and capabilities
- Revit API Documentation - Autodesk Revit API documentation
- Autodesk Revit Developer Guide - Autodesk Revit Developer Guide
- ifcopenshell Documentation - IfcOpenShell documentation for IFC processing
- pyRevit Documentation - pyRevit Developer Docs
Prompt engineering guide focusing on Cursor AI capabilities for professional BIM development